Knowledge-Enriched Data Management
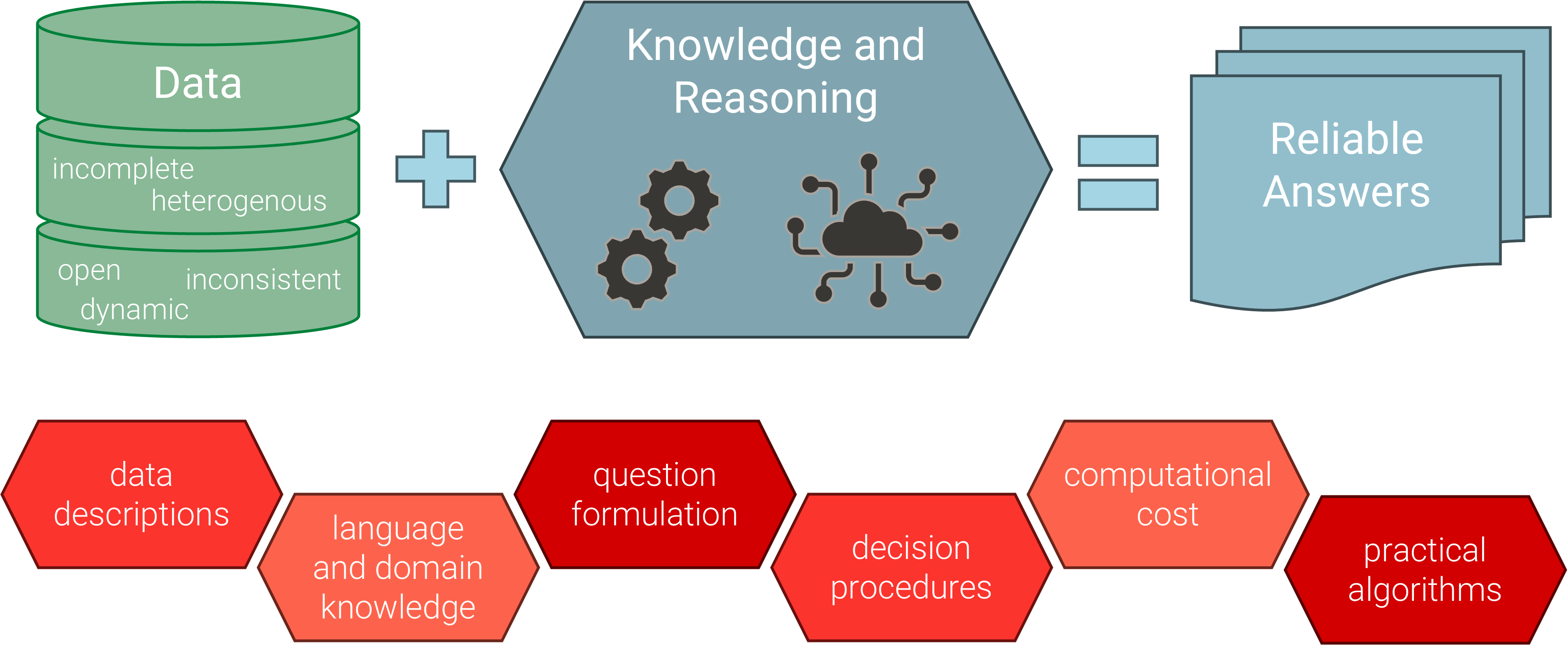
Knowledge-enriched data management focuses on designing and maintaining knowledge-aware, data-centric systems that support efficient, accurate, and transparent decision-making, even in the presence of incomplete, heterogeneous, or low-quality data. Our research focuses on developing robust theoretical foundations and practical methodologies in areas such as ontology-based data access, managing incomplete and inconsistent information, and Semantic Web technologies and their logical foundations. We strive to bridge symbolic and subsymbolic AI approaches, combining theoretical innovation with practical implementation to advance intelligent and explainable data management.
Ontology-Based Data Access
Ontology-Based Data Access (OBDA) is an approach that models and enhances data access and integration over heterogeneous and complex data sources by using a conceptual representation of the domain of interest, called an ontology. In this paradigm, users are freed from the need to understand the underlying structure of databases, software, and services. Instead, they interact with the system through the ontology, using it as a semantic layer that translates domain-specific queries into operations on the underlying datasets, ensuring seamless and efficient data access. Our research explores various aspects of OBDA, including ontology-mediated query answering, query rewriting techniques with respect to ontologies and mappings, optimization strategies for improving efficiency, and OBDA evolution, which explores adapting systems to dynamic data and knowledge.
Handling Incomplete or Inconsistent Information
Managing inconsistent and incomplete information is a critical challenge in knowledge-based systems, where issues can arise from missing or faulty data, conflicting sources, partial, inconsistent, or evolving knowledge. Our work focuses on developing robust theoretical and practical methods to ensure these systems can function effectively despite such imperfections, enabling reliable query answering, preserving integrity, and supporting robust and explainable decision-making in complex, real-world scenarios. This includes investigating repair-based approaches to identify minimal changes needed to restore consistency, inconsistency-tolerant semantics to derive plausible conclusions from partially consistent data, and advanced techniques for consistent query answering.
Semantic Web
The Semantic Web is an extension of the current web that enables machines to interpret and process data using foundational technologies like RDF (Resource Description Framework), OWL (Web Ontology Language), SHACL (Shapes Constraint Language), and SPARQL (query language for linked data). We study the theoretical and practical foundations of these semantic technologies and their relationships with other formalisms, such as description logics and databases. By advancing these techniques, we aim to develop intelligent approaches for web data management and reasoning.
